 |
coreboot
coreboot is an Open Source project aimed at replacing the proprietary BIOS found in most computers.
|
 |
coreboot
coreboot is an Open Source project aimed at replacing the proprietary BIOS found in most computers.
|
#include <commonlib/bsd/compression.h>#include <console/console.h>#include <bootmem.h>#include <program_loading.h>#include <fit.h>#include <endian.h>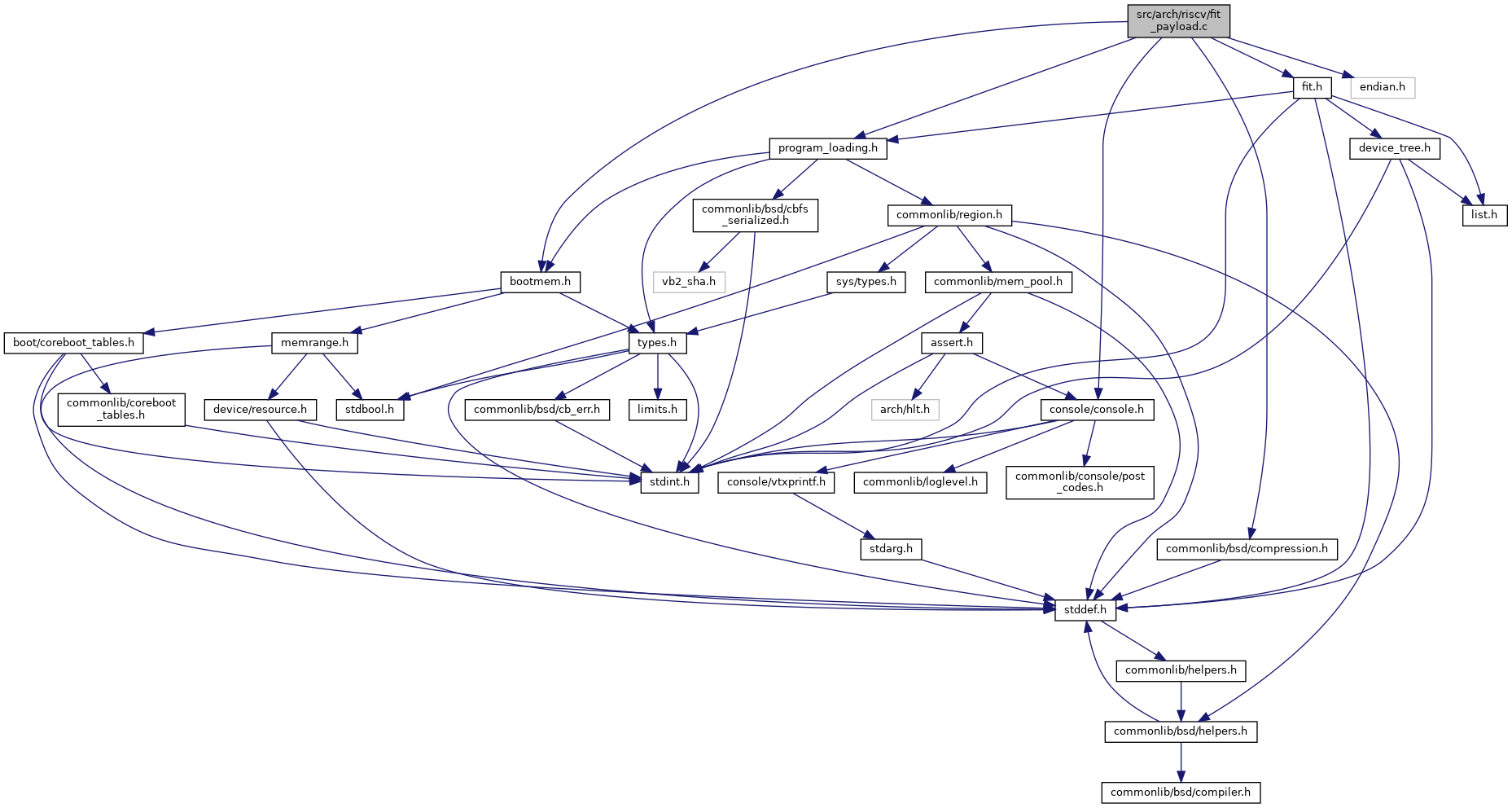
Go to the source code of this file.
Macros | |
| #define | MAX_KERNEL_SIZE (64*MiB) |
Functions | |
| static size_t | get_kernel_size (const struct fit_image_node *node) |
| static bool | fit_place_mem (const struct range_entry *r, void *arg) |
| Place the region in free memory range. More... | |
| bool | fit_payload_arch (struct prog *payload, struct fit_config_node *config, struct region *kernel, struct region *fdt, struct region *initrd) |
| #define MAX_KERNEL_SIZE (64*MiB) |
Definition at line 12 of file fit_payload.c.
| bool fit_payload_arch | ( | struct prog * | payload, |
| struct fit_config_node * | config, | ||
| struct region * | kernel, | ||
| struct region * | fdt, | ||
| struct region * | initrd | ||
| ) |
The kernel ARM documentation recommends loading the kernel above 32MiB in order to avoid the need to need to relocate prior to decompression.
The code assumes that bootmem_walk provides a sorted list of memory regions, starting from the lowest address. The order of the calls here doesn't matter, as the placement is enforced in the called functions. For details check code on top.
To ensure the fdt is not overwritten by the kernel decompressor, place the fdt above the 128 MB from the start of RAM, as recommended by the kernel documentation.
The code assumes that bootmem_walk provides a sorted list of memory regions, starting from the lowest address. The order of the calls here doesn't matter, as the placement is enforced in the called functions. For details check code on top.
NOTE: versions prior to v4.6 cannot make use of memory below the physical offset of the Image so it is recommended that the Image be placed as close as possible to the start of system RAM.
For kernel <v4.6 the INITRD and FDT can't be placed below the kernel. In that case set region offset to an address on top of kernel.
Definition at line 62 of file fit_payload.c.
References arg, BIOS_CRIT, BIOS_DEBUG, BM_MEM_PAYLOAD, bootmem_add_range(), bootmem_dump_ranges(), bootmem_walk(), config, fit_place_mem(), get_kernel_size(), NULL, region::offset, printk, prog_set_entry(), and region::size.
|
static |
Place the region in free memory range.
The caller has to set region->offset to the minimum allowed address.
Definition at line 43 of file fit_payload.c.
References ALIGN_UP, arg, BM_MEM_RAM, MAX, region::offset, range_entry_base(), range_entry_end(), range_entry_tag(), and region::size.
Referenced by fit_payload_arch().

|
static |
Definition at line 21 of file fit_payload.c.
References BIOS_INFO, MAX_KERNEL_SIZE, printk, and fit_image_node::size.
Referenced by fit_payload_arch().
