 |
coreboot
coreboot is an Open Source project aimed at replacing the proprietary BIOS found in most computers.
|
 |
coreboot
coreboot is an Open Source project aimed at replacing the proprietary BIOS found in most computers.
|
#include <acpi/acpi.h>#include <device/pci_ops.h>#include <bootmode.h>#include <console/console.h>#include <cpu/cpu.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <delay.h>#include <device/cardbus.h>#include <device/device.h>#include <device/pci.h>#include <device/pci_ids.h>#include <device/pcix.h>#include <device/pciexp.h>#include <lib.h>#include <pc80/i8259.h>#include <security/vboot/vbnv.h>#include <timestamp.h>#include <types.h>
Go to the source code of this file.
Enumerations | |
| enum | scan_state { PCI_ROUTE_CLOSE , PCI_ROUTE_SCAN , PCI_ROUTE_FINAL } |
Functions | |
| u8 | pci_moving_config8 (struct device *dev, unsigned int reg) |
| u16 | pci_moving_config16 (struct device *dev, unsigned int reg) |
| u32 | pci_moving_config32 (struct device *dev, unsigned int reg) |
| struct resource * | pci_get_resource (struct device *dev, unsigned long index) |
| Given a device and register, read the size of the BAR for that register. More... | |
| static void | pci_get_rom_resource (struct device *dev, unsigned long index) |
| Given a device and an index, read the size of the BAR for that register. More... | |
| size_t | pci_msix_table_size (struct device *dev) |
| Given a device, read the size of the MSI-X table. More... | |
| int | pci_msix_table_bar (struct device *dev, u32 *offset, u8 *idx) |
| Given a device, return the table offset and bar the MSI-X tables resides in. More... | |
| struct msix_entry * | pci_msix_get_table (struct device *dev) |
| Given a device, return a msix_entry pointer or NULL if no table was found. More... | |
| static unsigned int | get_rebar_offset (const struct device *dev, unsigned long index) |
| static uint64_t | get_rebar_sizes_mask (const struct device *dev, unsigned long index) |
| static void | pci_store_rebar_size (const struct device *dev, const struct resource *resource) |
| static void | configure_adjustable_base (const struct device *dev, unsigned long index, struct resource *res) |
| static void | pci_read_bases (struct device *dev, unsigned int howmany) |
| Read the base address registers for a given device. More... | |
| static void | pci_record_bridge_resource (struct device *dev, resource_t moving, unsigned int index, unsigned long type) |
| static void | pci_bridge_read_bases (struct device *dev) |
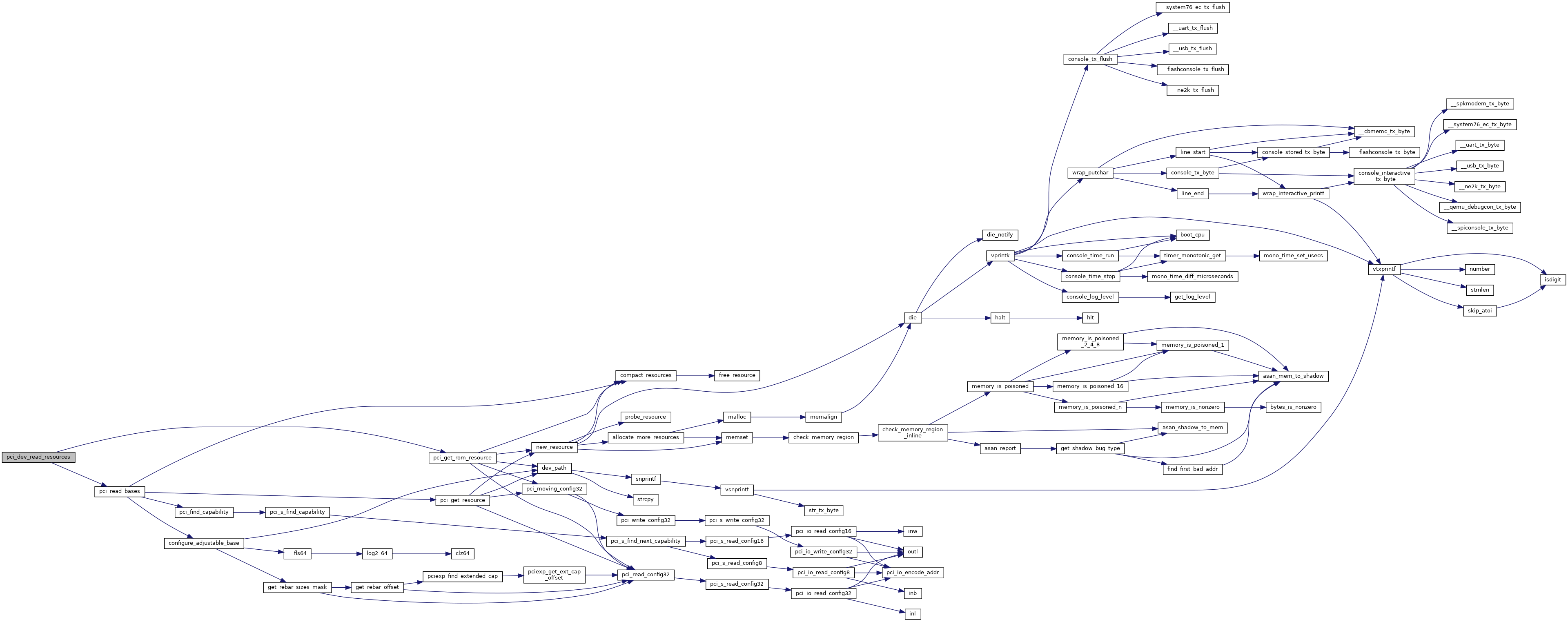
| void | pci_dev_read_resources (struct device *dev) |
| void | pci_bus_read_resources (struct device *dev) |
| void | pci_domain_read_resources (struct device *dev) |
| void | pci_domain_set_resources (struct device *dev) |
| static void | pci_store_resource (const struct device *const dev, const struct resource *const resource) |
| static void | pci_store_bridge_resource (const struct device *const dev, struct resource *const resource) |
| static void | pci_set_resource (struct device *dev, struct resource *resource) |
| void | pci_dev_set_resources (struct device *dev) |
| void | pci_dev_enable_resources (struct device *dev) |
| void | pci_bus_enable_resources (struct device *dev) |
| void | pci_bus_reset (struct bus *bus) |
| void | pci_dev_set_subsystem (struct device *dev, unsigned int vendor, unsigned int device) |
| static int | should_run_oprom (struct device *dev, struct rom_header *rom) |
| static int | should_load_oprom (struct device *dev) |
| static void | oprom_pre_graphics_stall (void) |
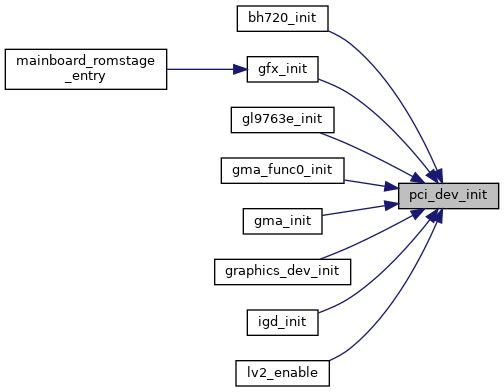
| void | pci_dev_init (struct device *dev) |
| Default handler: only runs the relevant PCI BIOS. More... | |
| static void | pci_bridge_vga_compat (struct bus *const bus) |
| Check for compatibility to route legacy VGA cycles through a bridge. More... | |
| static struct device_operations * | get_pci_bridge_ops (struct device *dev) |
| Detect the type of downstream bridge. More... | |
| static int | device_id_match (struct pci_driver *driver, unsigned short device_id) |
| Check if a device id matches a PCI driver entry. More... | |
| static void | set_pci_ops (struct device *dev) |
| Set up PCI device operation. More... | |
| static struct device * | pci_scan_get_dev (struct bus *bus, unsigned int devfn) |
| See if we have already allocated a device structure for a given devfn. More... | |
| struct device * | pci_probe_dev (struct device *dev, struct bus *bus, unsigned int devfn) |
| Scan a PCI bus. More... | |
| unsigned int | pci_match_simple_dev (struct device *dev, pci_devfn_t sdev) |
| Test for match between romstage and ramstage device instance. More... | |
| static void | pci_scan_hidden_device (struct device *dev) |
| PCI devices that are marked as "hidden" do not get probed. More... | |
| static bool | pci_bus_only_one_child (struct bus *bus) |
| A PCIe Downstream Port normally leads to a Link with only Device 0 on it (PCIe spec r5.0, sec 7.3.1). More... | |
| void | pci_scan_bus (struct bus *bus, unsigned int min_devfn, unsigned int max_devfn) |
| Scan a PCI bus. More... | |
| static void | pci_bridge_route (struct bus *link, scan_state state) |
| void | do_pci_scan_bridge (struct device *dev, void(*do_scan_bus)(struct bus *bus, unsigned int min_devfn, unsigned int max_devfn)) |
| Scan a PCI bridge and the buses behind the bridge. More... | |
| void | pci_scan_bridge (struct device *dev) |
| Scan a PCI bridge and the buses behind the bridge. More... | |
| void | pci_domain_scan_bus (struct device *dev) |
| Scan a PCI domain. More... | |
| void | pci_dev_disable_bus_master (const struct device *dev) |
| const char * | pin_to_str (int pin) |
| Take an INT_PIN number (0, 1 - 4) and convert it to a string ("NO PIN", "PIN A" - "PIN D") More... | |
| static int | swizzle_irq_pins (struct device *dev, struct device **parent_bridge) |
| Get the PCI INT_PIN swizzle for a device defined as: pin_parent = (pin_child + devn_child) % 4 + 1 where PIN A = 1 ... More... | |
| int | get_pci_irq_pins (struct device *dev, struct device **parent_bdg) |
| Given a device structure 'dev', find its interrupt pin and its parent bridge 'parent_bdg' device structure. More... | |
Variables | |
| struct pci_operations | pci_dev_ops_pci |
| Default device operation for PCI devices. More... | |
| struct device_operations | default_pci_ops_dev |
| struct device_operations | default_pci_ops_bus |
| Default device operations for PCI bridges. More... | |
| static struct device_operations | default_hidden_pci_ops_dev |
| Default device operations for PCI devices marked 'hidden'. More... | |
| enum scan_state |
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| PCI_ROUTE_CLOSE | |
| PCI_ROUTE_SCAN | |
| PCI_ROUTE_FINAL | |
Definition at line 1492 of file pci_device.c.
|
static |
Definition at line 379 of file pci_device.c.
References __fls64(), resource::align, resource::base, BIOS_ERR, BIOS_INFO, BIOS_WARNING, dev_path(), resource::flags, get_rebar_sizes_mask(), resource::gran, resource::index, IORESOURCE_PCI64, IORESOURCE_PCIE_RESIZABLE_BAR, resource::limit, printk, resource::size, UINT32_MAX, and UINT64_MAX.
Referenced by pci_read_bases().
|
static |
Check if a device id matches a PCI driver entry.
The driver entry can either point at a zero terminated array of acceptable device IDs, or include a single device ID.
| driver | pointer to the PCI driver entry being checked |
| device_id | PCI device ID of the device being matched |
Definition at line 1047 of file pci_device.c.
Referenced by set_pci_ops().
| void do_pci_scan_bridge | ( | struct device * | dev, |
| void(*)(struct bus *bus, unsigned int min_devfn, unsigned int max_devfn) | do_scan_bus | ||
| ) |
Scan a PCI bridge and the buses behind the bridge.
Determine the existence of buses behind the bridge. Set up the bridge according to the result of the scan.
This function is the default scan_bus() method for PCI bridge devices.
| dev | Pointer to the bridge device. |
| do_scan_bus | TODO |
Definition at line 1558 of file pci_device.c.
References BIOS_SPEW, bus::dev, dev_path(), die(), device::link_list, malloc(), memset(), NULL, pci_bridge_route(), pci_bridge_vga_compat(), PCI_ROUTE_FINAL, PCI_ROUTE_SCAN, and printk.
Referenced by byt_pciexp_scan_bridge(), and pci_scan_bridge().
|
static |
Detect the type of downstream bridge.
This function is a heuristic to detect which type of bus is downstream of a PCI-to-PCI bridge. This functions by looking for various capability blocks to figure out the type of downstream bridge. PCI-X, PCI-E, and Hypertransport all seem to have appropriate capabilities.
When only a PCI-Express capability is found the type is examined to see which type of bridge we have.
| dev | Pointer to the device structure of the bridge. |
Definition at line 994 of file pci_device.c.
References BIOS_DEBUG, CONFIG, default_pci_ops_bus, default_pciexp_hotplug_ops_bus, default_pciexp_ops_bus, default_pcix_ops_bus, dev_path(), PCI_CAP_ID_PCIE, PCI_CAP_ID_PCIX, PCI_EXP_FLAGS, PCI_EXP_FLAGS_TYPE, PCI_EXP_SLTCAP, PCI_EXP_SLTCAP_HPC, PCI_EXP_TYPE_DOWNSTREAM, PCI_EXP_TYPE_PCI_BRIDGE, PCI_EXP_TYPE_ROOT_PORT, PCI_EXP_TYPE_UPSTREAM, pci_find_capability(), pci_read_config16(), and printk.
Referenced by set_pci_ops().
Given a device structure 'dev', find its interrupt pin and its parent bridge 'parent_bdg' device structure.
If it is behind a bridge, it will return the interrupt pin number (1 - 4) of the parent bridge that the device interrupt pin has been swizzled to, otherwise it will return the interrupt pin that is programmed into the PCI config space of the target device. If 'dev' is behind a bridge, it will fill in 'parent_bdg' with the device structure of the bridge it is behind, otherwise it will copy 'dev' into 'parent_bdg'.
| dev | A PCI device structure to get interrupt pins for. |
| *parent_bdg | The PCI device structure for the bridge device 'dev' is attached to. |
Definition at line 1729 of file pci_device.c.
References BIOS_SPEW, BIOS_WARNING, device::bus, pci_path::devfn, DEVICE_PATH_PCI, device::enabled, NULL, device::path, device_path::pci, PCI_FUNC, PCI_INTERRUPT_PIN, pci_read_config8(), PCI_SLOT, pin_to_str(), printk, bus::secondary, swizzle_irq_pins(), and device_path::type.
Referenced by dnv_get_int_line(), write_pci_cfg_irqs(), and write_pci_config_irqs().
Definition at line 313 of file pci_device.c.
References resource::index, offset, PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_0, pci_read_config32(), PCI_REBAR_CTRL_IDX_MASK, PCI_REBAR_CTRL_NBARS_MASK, PCI_REBAR_CTRL_NBARS_SHIFT, PCI_REBAR_CTRL_OFFSET, PCIE_EXT_CAP_RESIZABLE_BAR, and pciexp_find_extended_cap().
Referenced by get_rebar_sizes_mask(), and pci_store_rebar_size().

Definition at line 341 of file pci_device.c.
References get_rebar_offset(), resource::index, offset, pci_read_config32(), PCI_REBAR_CAP_OFFSET, PCI_REBAR_CAP_SIZE_MASK, PCI_REBAR_CTRL_OFFSET, and PCI_REBAR_CTRL_SIZE_MASK.
Referenced by configure_adjustable_base().

Definition at line 866 of file pci_device.c.
References mdelay().

Definition at line 487 of file pci_device.c.
References compact_resources(), IORESOURCE_IO, IORESOURCE_MEM, IORESOURCE_PREFETCH, PCI_IO_BASE, PCI_IO_BASE_UPPER16, PCI_IO_LIMIT, PCI_IO_LIMIT_UPPER16, PCI_MEMORY_BASE, PCI_MEMORY_LIMIT, pci_moving_config16(), pci_moving_config32(), pci_moving_config8(), PCI_PREF_BASE_UPPER32, PCI_PREF_LIMIT_UPPER32, PCI_PREF_MEMORY_BASE, PCI_PREF_MEMORY_LIMIT, and pci_record_bridge_resource().
Referenced by pci_bus_read_resources().

|
static |
Definition at line 1498 of file pci_device.c.
References bus::bridge_cmd, device::bus, bus::dev, device::hotplug_buses, PCI_COMMAND, PCI_PRIMARY_BUS, pci_read_config16(), PCI_ROUTE_CLOSE, PCI_ROUTE_FINAL, PCI_ROUTE_SCAN, PCI_SECONDARY_BUS, PCI_STATUS, PCI_SUBORDINATE_BUS, pci_write_config16(), pci_write_config8(), bus::secondary, and bus::subordinate.
Referenced by do_pci_scan_bridge().
Check for compatibility to route legacy VGA cycles through a bridge.
Originally, when decoding i/o ports for legacy VGA cycles, bridges should only consider the 10 least significant bits of the port address. This means all VGA registers were aliased every 1024 ports! e.g. 0x3b0 was also decoded as 0x7b0, 0xbb0 etc.
To avoid this mess, a bridge control bit (VGA16) was introduced in 2003 to enable decoding of 16-bit port addresses. As we don't want to make this any more complex for now, we use this bit if possible and only warn if it's not supported (in set_vga_bridge_bits()).
Definition at line 956 of file pci_device.c.
References device::bus, bus::dev, bus::no_vga16, PCI_BRIDGE_CONTROL, PCI_BRIDGE_CTL_VGA, PCI_BRIDGE_CTL_VGA16, pci_read_config16(), and pci_write_config16().
Referenced by do_pci_scan_bridge().

Definition at line 758 of file pci_device.c.
References BIOS_DEBUG, bus::bridge_ctrl, device::command, dev_path(), device::link_list, PCI_BRIDGE_CONTROL, PCI_BRIDGE_CTL_PARITY, PCI_BRIDGE_CTL_SERR, PCI_BRIDGE_CTL_VGA, PCI_COMMAND_IO, pci_dev_enable_resources(), pci_read_config16(), pci_write_config16(), and printk.
A PCIe Downstream Port normally leads to a Link with only Device 0 on it (PCIe spec r5.0, sec 7.3.1).
As an optimization, scan only for Device 0 in that situation.
| bus | Pointer to the bus structure. |
Definition at line 1346 of file pci_device.c.
References bridge, bus::dev, DEVICE_PATH_PCI, PCI_CAP_ID_PCIE, PCI_EXP_FLAGS, PCI_EXP_FLAGS_TYPE, pci_find_capability(), pci_read_config16(), and pciexp_is_downstream_port().
Referenced by pci_scan_bus().

Definition at line 540 of file pci_device.c.
References pci_bridge_read_bases(), pci_get_rom_resource(), pci_read_bases(), and PCI_ROM_ADDRESS1.
Definition at line 777 of file pci_device.c.
References delay(), bus::dev, mdelay(), PCI_BRIDGE_CONTROL, PCI_BRIDGE_CTL_BUS_RESET, pci_read_config16(), and pci_write_config16().
Definition at line 1616 of file pci_device.c.
References bus::dev, PCI_COMMAND, PCI_COMMAND_MASTER, and pci_update_config16().
Referenced by tbt_finalize().
Definition at line 721 of file pci_device.c.
References BIOS_DEBUG, device::command, dev_path(), NULL, device::on_mainboard, ops, device::ops, device_operations::ops_pci, PCI_COMMAND, PCI_DEVICE_ID, pci_read_config16(), PCI_VENDOR_ID, pci_write_config16(), printk, device::subsystem_device, and device::subsystem_vendor.
Referenced by cardbus_enable_resources(), hudson_lpc_enable_resources(), lpc_enable_resources(), and pci_bus_enable_resources().
Default handler: only runs the relevant PCI BIOS.
Definition at line 873 of file pci_device.c.
Referenced by bh720_init(), gfx_init(), gl9763e_init(), gma_func0_init(), gma_init(), graphics_dev_init(), igd_init(), and lv2_enable().
Definition at line 534 of file pci_device.c.
References pci_get_rom_resource(), pci_read_bases(), and PCI_ROM_ADDRESS.
Referenced by aspeed_ast2050_read_resources(), gma_func0_read_resources(), gma_read_resources(), hudson_lpc_read_resources(), i82801gx_lpc_read_resources(), i82801ix_lpc_read_resources(), i82801jx_lpc_read_resources(), iommu_read_resources(), lpc_read_resources(), lpe_read_resources(), mc_read_resources(), mmapvtd_read_resources(), nc_read_resources(), pch_lpc_read_resources(), pch_pmc_read_resources(), sata_read_resources(), sc_read_resources(), smbus_read_resources(), and systemagent_read_resources().
Definition at line 691 of file pci_device.c.
References assign_resources(), bus::children, bus::dev, device::hdr_type, device::link_list, bus::next, resource::next, PCI_CACHE_LINE_SIZE, PCI_HEADER_TYPE_BRIDGE, PCI_INTERRUPT_LINE, PCI_INTERRUPT_PIN, PCI_LATENCY_TIMER, pci_read_config8(), PCI_SEC_LATENCY_TIMER, pci_set_resource(), pci_write_config8(), and device::resource_list.
Referenced by graphics_set_resources(), hudson_lpc_set_resources(), lpc_set_resources(), nb_set_resources(), rl5c476_set_resources(), and sata_set_resources().
Definition at line 791 of file pci_device.c.
References device::hdr_type, offset, PCI_CAP_ID_SSVID, PCI_CB_SUBSYSTEM_VENDOR_ID, pci_find_capability(), PCI_HEADER_TYPE_BRIDGE, PCI_HEADER_TYPE_CARDBUS, PCI_HEADER_TYPE_NORMAL, pci_read_config32(), PCI_SUBSYSTEM_VENDOR_ID, PCI_VENDOR_ID, pci_write_config32(), and vendor.
Referenced by usb_ehci_set_subsystem().

Definition at line 547 of file pci_device.c.
References cpu_phys_address_size(), resource::flags, IOINDEX_SUBTRACTIVE, IORESOURCE_ASSIGNED, IORESOURCE_IO, IORESOURCE_MEM, IORESOURCE_SUBTRACTIVE, resource::limit, and new_resource().
Referenced by cpu_pci_domain_read_resources(), domain_read_resources(), i440bx_domain_read_resources(), mch_domain_read_resources(), and xeonsp_pci_domain_read_resources().
Scan a PCI domain.
This function is the default scan_bus() method for PCI domains.
| dev | Pointer to the domain. |
Definition at line 1610 of file pci_device.c.
References bus::dev, device::link_list, PCI_DEVFN, and pci_scan_bus().
Definition at line 564 of file pci_device.c.
References assign_resources(), and device::link_list.
Referenced by mtk_pcie_domain_set_resources().
Given a device and register, read the size of the BAR for that register.
| dev | Pointer to the device structure. |
| index | Address of the PCI configuration register. |
Definition at line 86 of file pci_device.c.
References resource::align, BIOS_DEBUG, BIOS_ERR, dev_path(), resource::flags, resource::gran, resource::index, IORESOURCE_IO, IORESOURCE_MEM, IORESOURCE_PCI64, IORESOURCE_PREFETCH, resource::limit, new_resource(), PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_ATTR_MASK, PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_LIMIT_1M, PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_LIMIT_32, PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_LIMIT_64, PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_LIMIT_MASK, PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_PREFETCH, PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_SPACE_IO, pci_moving_config32(), pci_read_config32(), printk, resource::size, and value.
Referenced by cardbus_read_resources(), and pci_read_bases().
Given a device and an index, read the size of the BAR for that register.
| dev | Pointer to the device structure. |
| index | Address of the PCI configuration register. |
Definition at line 201 of file pci_device.c.
References resource::align, BIOS_DEBUG, compact_resources(), dev_path(), resource::flags, resource::gran, resource::index, IORESOURCE_MEM, IORESOURCE_READONLY, resource::limit, new_resource(), pci_moving_config32(), pci_read_config32(), PCI_ROM_ADDRESS_ENABLE, printk, resource::size, and value.
Referenced by pci_bus_read_resources(), and pci_dev_read_resources().
| unsigned int pci_match_simple_dev | ( | struct device * | dev, |
| pci_devfn_t | sdev | ||
| ) |
Test for match between romstage and ramstage device instance.
| dev | Pointer to the device structure. |
| sdev | Simple device model identifier, created with PCI_DEV(). |
Definition at line 1293 of file pci_device.c.
References device::bus, pci_path::devfn, device::path, device_path::pci, PCI_DEV2DEVFN, PCI_DEV2SEGBUS, and bus::secondary.
Definition at line 45 of file pci_device.c.
References pci_read_config16(), pci_write_config16(), and value.
Referenced by pci_bridge_read_bases().

Definition at line 62 of file pci_device.c.
References pci_read_config32(), pci_write_config32(), and value.
Referenced by cardbus_read_resources(), pci_bridge_read_bases(), pci_get_resource(), and pci_get_rom_resource().

Definition at line 28 of file pci_device.c.
References pci_read_config8(), pci_write_config8(), and value.
Referenced by pci_bridge_read_bases().

| struct msix_entry* pci_msix_get_table | ( | struct device * | dev | ) |
Given a device, return a msix_entry pointer or NULL if no table was found.
| dev | Pointer to the device structure. |
Definition at line 290 of file pci_device.c.
References resource::base, resource::flags, IORESOURCE_PCI64, NULL, offset, PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_0, pci_msix_table_bar(), probe_resource(), and resource::size.
Given a device, return the table offset and bar the MSI-X tables resides in.
| dev | Pointer to the device structure. |
| offset | Returned value gives the offset in bytes inside the PCI BAR. |
| idx | The returned value is the index of the PCI_BASE_ADDRESS register the MSI-X table is located in. |
Definition at line 270 of file pci_device.c.
References offset, PCI_CAP_ID_MSIX, pci_find_capability(), PCI_MSIX_PBA_BIR, PCI_MSIX_PBA_OFFSET, PCI_MSIX_TABLE, and pci_read_config32().
Referenced by ecam0_pci_enable_msix(), and pci_msix_get_table().

Given a device, read the size of the MSI-X table.
| dev | Pointer to the device structure. |
Definition at line 251 of file pci_device.c.
References PCI_CAP_ID_MSIX, pci_find_capability(), PCI_MSIX_FLAGS, PCI_MSIX_FLAGS_QSIZE, and pci_read_config16().
Referenced by ecam0_pci_enable_msix().
Scan a PCI bus.
Determine the existence of a given PCI device. Allocate a new struct device if dev==NULL was passed in and the device exists in hardware.
| dev | Pointer to the dev structure. |
| bus | Pointer to the bus structure. |
| devfn | A device/function number to look at. |
Definition at line 1183 of file pci_device.c.
References alloc_dev(), BIOS_DEBUG, BIOS_INFO, BIOS_SPEW, device::bus, device::chip_ops, device::class, device::command, CONFIG, dev_path(), pci_path::devfn, device::device, DEVICE_PATH_PCI, device_operations::enable, chip_operations::enable_dev, device::enabled, device::hdr_type, NULL, device::ops, device::path, device_path::pci, PCI_BASE_CLASS_SYSTEM, PCI_CLASS_REVISION, PCI_COMMAND_MASTER, PCI_HEADER_TYPE, pci_read_config32(), pci_read_config8(), PCI_VENDOR_ID, printk, set_pci_ops(), device_path::type, and device::vendor.
Referenced by cpu_bus_scan(), ecam0_fix_missing_devices(), pci_scan_bus(), and xeonsp_pci_domain_scan_bus().
Read the base address registers for a given device.
| dev | Pointer to the dev structure. |
| howmany | How many registers to read (6 for device, 2 for bridge). |
Definition at line 440 of file pci_device.c.
References compact_resources(), CONFIG, configure_adjustable_base(), resource::flags, resource::index, IORESOURCE_PCI64, PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_0, PCI_CAP_ID_PCIE, pci_find_capability(), and pci_get_resource().
Referenced by pci_bus_read_resources(), and pci_dev_read_resources().
|
static |
Definition at line 459 of file pci_device.c.
References resource::align, resource::flags, resource::gran, resource::index, IORESOURCE_BRIDGE, IORESOURCE_PCI_BRIDGE, resource::limit, new_resource(), NULL, resource::size, and type.
Referenced by pci_bridge_read_bases().

Scan a PCI bridge and the buses behind the bridge.
Determine the existence of buses behind the bridge. Set up the bridge according to the result of the scan.
This function is the default scan_bus() method for PCI bridge devices.
| dev | Pointer to the bridge device. |
Definition at line 1598 of file pci_device.c.
References bus::dev, do_pci_scan_bridge(), and pci_scan_bus().
Scan a PCI bus.
Determine the existence of devices and bridges on a PCI bus. If there are bridges on the bus, recursively scan the buses behind the bridges.
| bus | Pointer to the bus structure. |
| min_devfn | Minimum devfn to look at in the scan, usually 0x00. |
| max_devfn | Maximum devfn to look at in the scan, usually 0xff. |
Definition at line 1379 of file pci_device.c.
References BIOS_DEBUG, BIOS_ERR, BIOS_WARNING, bus::children, CONFIG, dev_path(), DEVICE_PATH_PCI, enable_static_device(), device::enabled, device::hdr_type, device::hidden, device::mandatory, MIN, device::path, pci_bus_only_one_child(), PCI_FUNC, pci_probe_dev(), pci_scan_get_dev(), pci_scan_hidden_device(), pcidev_path_behind(), post_code, printk, scan_bridges(), bus::secondary, device::sibling, device_path::type, and device::vendor.
Referenced by pci_domain_scan_bus(), pci_scan_bridge(), pciexp_scan_bus(), and xeonsp_pci_domain_scan_bus().
See if we have already allocated a device structure for a given devfn.
Given a PCI bus structure and a devfn number, find the device structure corresponding to the devfn, if present. Then move the device structure as the last child on the bus.
| bus | Pointer to the bus structure. |
| devfn | A device/function number. |
Definition at line 1134 of file pci_device.c.
References bus::children, pci_path::devfn, DEVICE_PATH_PCI, NULL, device::path, device_path::pci, device::sibling, and device_path::type.
Referenced by pci_scan_bus().
PCI devices that are marked as "hidden" do not get probed.
However, the same initialization logic is still performed as if it were. This is useful when devices would like to be described in the devicetree.cb file, and/or present static PCI resources to the allocator, but the platform firmware hides the device (makes the device invisible to PCI enumeration) before PCI enumeration takes place.
The expected semantics of PCI devices marked as 'hidden': 1) The device is actually present under the specified BDF 2) The device config space can still be accessed somehow, but the Vendor ID indicates there is no device there (it reads as 0xffffffff). 3) The device may still consume PCI resources. Typically, these would have been hardcoded elsewhere.
| dev | Pointer to the device structure. |
Definition at line 1316 of file pci_device.c.
References BIOS_DEBUG, device::chip_ops, default_hidden_pci_ops_dev, dev_path(), device::device, device_operations::enable, chip_operations::enable_dev, NULL, device::ops, and printk.
Referenced by pci_scan_bus().
Definition at line 631 of file pci_device.c.
References BIOS_ERR, device::command, CONFIG, dev_path(), resource::flags, resource::index, IORESOURCE_ASSIGNED, IORESOURCE_BRIDGE, IORESOURCE_FIXED, IORESOURCE_IO, IORESOURCE_MEM, IORESOURCE_PCI_BRIDGE, IORESOURCE_PCIE_RESIZABLE_BAR, IORESOURCE_STORED, IORESOURCE_SUBTRACTIVE, PCI_COMMAND_IO, PCI_COMMAND_MASTER, PCI_COMMAND_MEMORY, pci_store_bridge_resource(), pci_store_rebar_size(), pci_store_resource(), printk, report_resource_stored(), resource_type(), and resource::size.
Referenced by pci_dev_set_resources().
|
static |
Definition at line 589 of file pci_device.c.
References resource::base, base, BIOS_ERR, resource::flags, resource::gran, resource::index, IORESOURCE_STORED, resource::limit, PCI_IO_BASE, PCI_IO_BASE_UPPER16, PCI_IO_LIMIT, PCI_IO_LIMIT_UPPER16, PCI_MEMORY_BASE, PCI_MEMORY_LIMIT, PCI_PREF_BASE_UPPER32, PCI_PREF_LIMIT_UPPER32, PCI_PREF_MEMORY_BASE, PCI_PREF_MEMORY_LIMIT, pci_write_config16(), pci_write_config32(), pci_write_config8(), printk, resource_end(), and resource::size.
Referenced by pci_set_resource().
|
static |
Definition at line 366 of file pci_device.c.
References __fls64(), get_rebar_offset(), resource::index, offset, PCI_REBAR_CTRL_OFFSET, PCI_REBAR_CTRL_SIZE_MASK, PCI_REBAR_CTRL_SIZE_SHIFT, pci_update_config32(), and resource::size.
Referenced by pci_set_resource().

|
static |
Definition at line 569 of file pci_device.c.
References resource::base, resource::flags, resource::index, IORESOURCE_IO, IORESOURCE_PCI64, PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_SPACE_IO, and pci_write_config32().
Referenced by pci_set_resource().

| const char* pin_to_str | ( | int | pin | ) |
Take an INT_PIN number (0, 1 - 4) and convert it to a string ("NO PIN", "PIN A" - "PIN D")
| pin | PCI Interrupt Pin number (0, 1 - 4) |
Definition at line 1628 of file pci_device.c.
Referenced by assign_pci_irqs(), get_pci_irq_pins(), swizzle_irq_pins(), write_pci_cfg_irqs(), and write_pci_config_irqs().
Set up PCI device operation.
Check if it already has a driver. If not, use find_device_operations(), or set to a default based on type.
| dev | Pointer to the device whose pci_ops you want to set. |
Definition at line 1069 of file pci_device.c.
References BIOS_ERR, BIOS_SPEW, device::class, default_cardbus_ops_bus, default_pci_ops_dev, dev_path(), device::device, device_id_match(), device::enabled, get_pci_bridge_ops(), device::hdr_type, device::ops, PCI_CLASS_BRIDGE_PCI, PCI_HEADER_TYPE_BRIDGE, PCI_HEADER_TYPE_CARDBUS, PCI_HEADER_TYPE_NORMAL, printk, and device::vendor.
Referenced by pci_probe_dev().
|
static |
Definition at line 850 of file pci_device.c.
References acpi_is_wakeup_s3(), device::class, CONFIG, NULL, PCI_CLASS_DISPLAY_VGA, and should_run_oprom().
|
static |
Definition at line 823 of file pci_device.c.
References BIOS_DEBUG, CONFIG, display_init_required(), NULL, printk, and verified_boot_should_run_oprom().
Referenced by should_load_oprom().

Get the PCI INT_PIN swizzle for a device defined as: pin_parent = (pin_child + devn_child) % 4 + 1 where PIN A = 1 ...
PIN_D = 4
Given a PCI device structure 'dev', find the interrupt pin that will be triggered on its parent bridge device when generating an interrupt. For example: Device 1:3.2 may use INT_PIN A but will trigger PIN D on its parent bridge device. In this case, this function will return 4 (PIN D).
| dev | A PCI device structure to swizzle interrupt pins for |
| *parent_bridge | The PCI device structure for the bridge device 'dev' is attached to |
Definition at line 1661 of file pci_device.c.
References BIOS_SPEW, device::bus, bus::dev, pci_path::devfn, device::path, device_path::pci, PCI_FUNC, PCI_INTERRUPT_PIN, pci_read_config8(), PCI_SLOT, pin_to_str(), printk, and bus::secondary.
Referenced by get_pci_irq_pins().
|
static |
Default device operations for PCI devices marked 'hidden'.
Definition at line 873 of file pci_device.c.
Referenced by pci_scan_hidden_device().
| struct device_operations default_pci_ops_bus |
Default device operations for PCI bridges.
Definition at line 873 of file pci_device.c.
Referenced by get_pci_bridge_ops().
| struct device_operations default_pci_ops_dev |
Definition at line 873 of file pci_device.c.
Referenced by set_pci_ops().
| struct pci_operations pci_dev_ops_pci |
Default device operation for PCI devices.
Definition at line 873 of file pci_device.c.